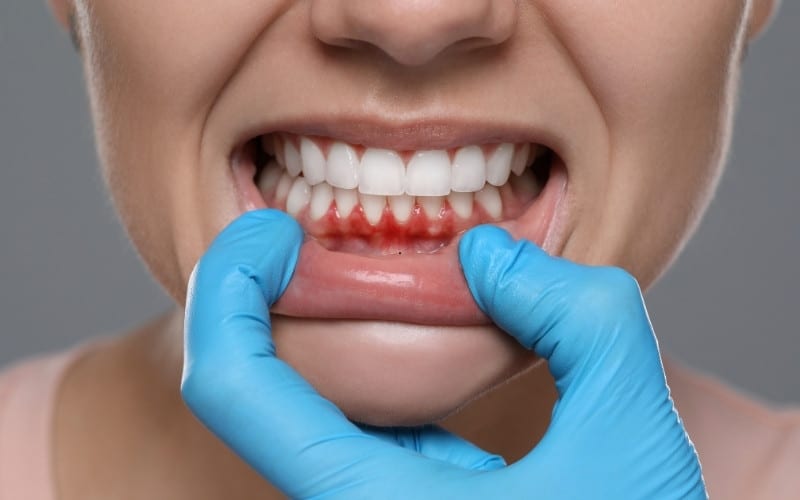
Gum recession is a common dental issue that many people overlook. This condition occurs when the gum tissue pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or even the tooth root. Early recognition of gum recession is vital for preventing further complications. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth sensitivity, increased cavities, and even tooth loss.
Many individuals may not realize they have gum recession until they experience discomfort or pain. Being aware of the signs allows for timely intervention and helps maintain your overall oral health.
This blog will explore the signs and symptoms of gum recession and how to address this issue effectively.
Understanding Gum Recession
Gum recession is when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away. This condition exposes the tooth roots and can lead to various dental issues. Common causes of gum recession include periodontal disease, aggressive brushing, tobacco use, and hormonal changes.
The anatomy of the gums plays a crucial role in oral health. Healthy gums protect the roots of your teeth and help keep them firmly in place. The protective barrier is compromised when gum recession occurs, leading to heightened sensitivity and potential tooth decay.
Unlike other gum diseases, this issue is not always accompanied by inflammation or pain. Some people may not even realize they have it until more serious issues develop.
Identifying gum recession early is essential for effective treatment and maintaining good oral hygiene. Regular dental check-ups can help spot changes in gum health. By understanding gum recession, you can take proactive measures to safeguard your smile.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Recession
Visible Changes in Gums
One of the first signs of gum recession is visible changes in the gum line. You may notice that your gums appear to pull away from your teeth, creating noticeable gaps. These gaps can lead to exposed tooth roots, increasing the risk of decay.
Additionally, the color or texture of your gums may change. Healthy gums are usually pink and firm, while receding gums may appear red or inflamed.
Tooth Sensitivity
As gums recede, the tooth roots become exposed. This exposure can increase sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods. You may experience discomfort when consuming beverages or foods at varying temperatures. If you find yourself avoiding your favorite snacks due to sensitivity, it may be a sign of gum recession.
Longer-Looking Teeth
Another noticeable symptom of this problem is the appearance of longer teeth. As the gum tissue recedes, it reveals more of the tooth’s root, making the teeth seem elongated. This change can affect your smile’s aesthetics and contribute to feelings of self-consciousness.
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can indicate various oral health issues, including gum recession. If you notice bleeding while brushing or flossing, it is essential to pay attention. This bleeding can result from gum inflammation or irritation, both of which can accompany receding gums. Do not ignore this sign. It may indicate a need for professional dental care.
Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath can be another sign of this issue. As bacteria build up in the exposed areas of the gums, they can produce foul-smelling compounds. If you notice bad breath despite regular brushing and flossing, gum recession may be to blame.
Pain or Discomfort
This problem may lead to pain or discomfort in the affected areas. If you experience ongoing pain, it could indicate that your gums are receding. This discomfort often worsens during brushing or when consuming certain foods. Ignoring pain can worsen the problem, so pay attention to these signals from your body.
Identifying Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing gum recession. Understanding these risks can help you take preventive measures.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in oral health. You may be at higher risk if your family members have suffered from gum recession.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Failing to maintain proper oral hygiene can lead to plaque buildup. This buildup can contribute to gum disease, ultimately resulting in recession.
Tobacco Use
Tobacco products can damage your gums and lead to gum recession. Smoking or using chewing tobacco increases the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes can affect gum health. Women may experience gum issues during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, making them more susceptible to recession.
Teeth Grinding
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, places excessive pressure on the gums and teeth. Over time, this pressure can lead to gum recession.
Misaligned Teeth
Misalignment can cause uneven pressure on the gums. If your teeth are not properly aligned, certain areas may experience more wear and tear, increasing the risk of recession.
Aggressive Brushing Techniques
Brushing your teeth too hard can wear away gum tissue. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle strokes to avoid damaging your gums.
By understanding these risk factors, you can proactively protect your gums. Regular dental visits can help identify potential issues before they become serious.
When to See a Dentist?
If you notice any signs of this issue, it is time to visit your dentist. Schedule an appointment for periodontal treatment in Oak Forest if you experience visible changes in your gums, tooth sensitivity, or bleeding. Your dentist will perform a thorough examination to determine the severity of your condition.
During your visit, they may use diagnostic tools such as probing and X-rays. Probing involves measuring the depth of the gum pockets around your teeth. X-rays can help visualize bone loss and other underlying issues. Identifying the extent of this problem is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment.
Prevention and Treatment Options
Prevention Tips
Maintain proper oral hygiene to prevent this problem. Brush your teeth at least twice daily and floss daily to remove plaque. Regular dental check-ups are vital for identifying issues early. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals also supports gum health. Avoiding tobacco products can significantly reduce your risk of gum disease and recession.
Treatment Options
If gum recession occurs, several treatment options are available. Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line. In more severe cases, gum grafting may be necessary. This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth and attaching it to the receded area.
A dental professional will create a personalized treatment plan based on the severity of your gum recession. Following their recommendations is essential for restoring your gum health and preventing further issues.
Recognizing the signs of this issue is essential for maintaining your oral health. You can take proactive steps by being aware of symptoms like sensitivity and visible changes in your gums. Regular dental check-ups will help ensure your gums remain healthy. Do not ignore the signs. Schedule a dental visit today.